 Dust
Emission and Polarization of Orion A Giant Molecular Cloud filament
observed using SHARCII and Hertz
Dust
Emission and Polarization of Orion A Giant Molecular Cloud filament
observed using SHARCII and Hertz 
Astronomers led by Dr. Martin Houde at the Caltech Submillimeter
Observatory
reported sensitive polarization measurements
using the Herz, 350 micron submillimeter polarimeter , and
the SHARCII sensitive submillimeter camera, as well as HCN and HCO+
spectroscopic observations to trace the orientation of the magnetic
field in the Orion A
star-forming region. The polarimetry data allowed them to trace
the
direction of the projection of the magnetic field in the plane of the
sky relative to the orientation of the integral-shaped filament.
The direction of the projection of the magnetic field was
found to vary
considerably as one moves from north to south. The result was
published by Houde
et al. 2004 in Astrophysical Journal.
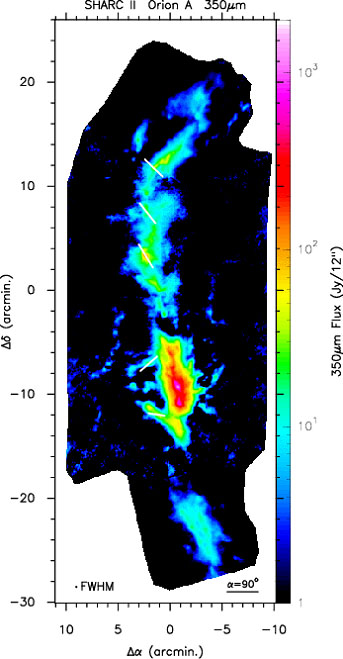
Figure 1. 350  m continuum map of the Orion
A region obtained with SHARC II. The orientation
of the magnetic field is indicated at five
positions along the ISF on the map. The
projection of the magnetic field in the plane
of the sky is also shown by the orientation of
the accompanying vectors, and the inclination
angle is given by the length of the vectors,
using the scale shown in the bottom right
corner. The beamwidth is shown in the lower
left corner (~12") and the reference position
is at R.A.= 5h32m50s,
decl.= -5deg 15' 00" (B1950.0).
m continuum map of the Orion
A region obtained with SHARC II. The orientation
of the magnetic field is indicated at five
positions along the ISF on the map. The
projection of the magnetic field in the plane
of the sky is also shown by the orientation of
the accompanying vectors, and the inclination
angle is given by the length of the vectors,
using the scale shown in the bottom right
corner. The beamwidth is shown in the lower
left corner (~12") and the reference position
is at R.A.= 5h32m50s,
decl.= -5deg 15' 00" (B1950.0).
Go back to A Digest of Recent News and
Scientific Results at the Caltech Submillimeter Observatory

 Dust
Emission and Polarization of Orion A Giant Molecular Cloud filament
observed using SHARCII and Hertz
Dust
Emission and Polarization of Orion A Giant Molecular Cloud filament
observed using SHARCII and Hertz 

 Dust
Emission and Polarization of Orion A Giant Molecular Cloud filament
observed using SHARCII and Hertz
Dust
Emission and Polarization of Orion A Giant Molecular Cloud filament
observed using SHARCII and Hertz 
 m continuum map of the Orion
A region obtained with SHARC II. The orientation
of the magnetic field is indicated at five
positions along the ISF on the map. The
projection of the magnetic field in the plane
of the sky is also shown by the orientation of
the accompanying vectors, and the inclination
angle is given by the length of the vectors,
using the scale shown in the bottom right
corner. The beamwidth is shown in the lower
left corner (~12") and the reference position
is at R.A.= 5h32m50s,
decl.= -5deg 15' 00" (B1950.0).
m continuum map of the Orion
A region obtained with SHARC II. The orientation
of the magnetic field is indicated at five
positions along the ISF on the map. The
projection of the magnetic field in the plane
of the sky is also shown by the orientation of
the accompanying vectors, and the inclination
angle is given by the length of the vectors,
using the scale shown in the bottom right
corner. The beamwidth is shown in the lower
left corner (~12") and the reference position
is at R.A.= 5h32m50s,
decl.= -5deg 15' 00" (B1950.0).